(a) State two factors that affect the rate of evaporation of a liquid.
(b) Explain the term latent heal.
(c) Explain each of the following phenomena:
(i) On a dry day, water in a clay pot is cooler than water in a rubber container:
(ii) Cooking of food is faster in a pressure cooker than in an ordinary pot.
(d) A 40 V electric heater is used to supply a current of 12 A for 1400 seconds to a body mass of 1.5 kg at its melting point. The body melts and its temperature rises by 60°C in an extra 1.2 minutes, Calculate the:
(i) Latent heat of fusion of the body
(ii) Specific heat capacity of the body.
(e) State two differences between evaporation and boiling.
(a)(i) What is meant by the term artificial radioactivity?
(ii) Complete the table below
| Emission | Nature | Charge | Ionizing |
| High speed electron | Moderately ionizing | ||
| Neutral | Negligible ionizing ability | ||
| Alpha particles | Positive |
(b) In an x-ray tube, an electron is accelerated from rest towards a metal target by a 30 kV source. Calculate the kinetic energy of the electron. [e=1.6 x 10\(^{-19}\)C]
(c) The table below shows the frequencies of radiations incident on a certain metal and the corresponding kinetic energies of the photoelectrons.
| Frequency x 10\(^{14}\)(Hz) | 6.8 | 8.0 | 9.2 | 10.0 | 11.0 |
| Kinetic energy x 10\(^{-19}\)(j) | 0.8 | 1.6 | 2.4 | 2.9 | 3.8 |
(i) Plot a graph of kinetic energy, K.E, on the vertical axis and frequency, f, on the horizontal axis starting both axes from the origin (0,0).
(ii) From the graph, determine the:
i. Planck's constant;
ii. Threshold frequency of radiations;
iii. Work function of the metal.
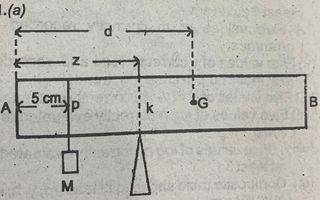
You are provided with a metre rule, a weight hanger, slotted masses, M, a piece (if string, a weighing balance and a knife edge. Use the diagram above as a guide to perform the experiment.
(i) Using the weighing balance, determine and record the mass, M\(_{o}\), of the unloaded metre rule.
(ii) Determine and record the mass, m, of the weight hanger.
(ii) Suspend the metre rule horizontally on the knife edge. Adjust the knife edge to a point G on the metre rule where it balances horizontally.
(iv) Record the distance, d = AG.
(v) Suspend the weight hanger securely at a point, P, on the metre rule such that AP= 5 cm. Keep the hanger at this point throughout the experiment
(vi) Add a mass, M = 20 g to the hanger, adjust the knife edge to a point K on the metre rule such that it balances horizontally as shown in the diagram above.
(vii) Determine and record the distance z = AK.
(vii) Record M and evaluate y - (z - 5), x - (d - z] and v = \(\frac{x}{y}\)
(ix) Repeat the experiment for M = 40 g, 60 g, 80 g and 100 g. In each case, evaluate y, x and v.
(x) Tabulate the results.
(xi) Plot a graph with M on the vertical axis and v on the horizontal axis, sinning both axes from the origin (0,0).
(xii) Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
(xii) Determine the intercept, c, on the vertical axis.
(xiv) State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b) (i) Under what condition is an object said to be in a stable equilibrium
(ii) Auniform beam of weight 50 N has a body of weight 100 N hung at one end of it. If the beam is 12 m long, determine the distance of a support from a 100 N body for it to balance horizontally.
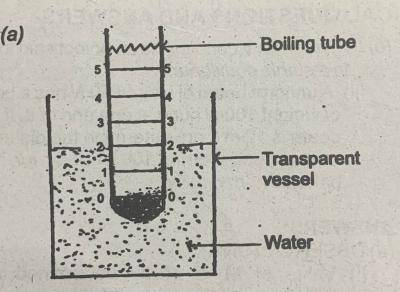
You are provided with a loaded boiling tube with a centimeter scale fixed inside it, a transparent vessel filled with water, standard masses 2 g, 5g and 10 g, and a slide vernier caliper. Use the diagram above as a guide to perform the experiment.
(i) Use the slide vernier caliper to measure and record the external diameter, D, of the boiling tube.
(ii) Evaluated A = 0.25\(\pi\)D\(^{2}\), where \(\pi\) = 3.14.
(iii) Place the loaded boiling tube gently in the water in the transparent vessel such that it floats vertically.
(iv) Read and record the depth of immersion, y, from the zero mark of the scale fixed inside, the boiling tube.
(v) Add a mass, m = 2g, to the boiling tube. Read and record the new depth of immersion, y, from the zero mark of the scale.
(vi) Evaluate h = (y - y\(_{0}\)), log h and log m.
(vii) Repeat the experiment for four other values of m = 5g, 7g, 10 g, and 12g. In each case, record y and evaluate h, log h, and log m.
(viii) Tabulate the results.
(ix) Plot a graph with log m on the vertical axis and log h on the horizontal axis starting both axes from the origin (0,0).
(b)(i) State in full the law on which the experiment in (a) is based.
(ii) A uniform cylindrical rod is 0.63 m long and it has a cross-sectional area of 0.1 m\(^{2}\). Calculate the depth of immersion of the rod if it floats vertically in a liquid of relative density 1.26. [density of rod =720 kg m\(^{-3}\), g = 10 m s\(^{-2}\)].
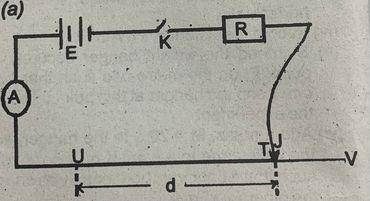
You are provided with a battery of e.m.f, E, a standard resistor, R, of resistance 2 \(\Omega\), a key, K, an ammeter, A, a jockey, J, a potentiometer, UV, and some connecting wires.
(i) Measure and record the emf, E, of the battery.
(ii) Set up the circuit as shown in the diagram above with the key open.
(iii) Place the jockey at the point, U, of the potentiometer wire. Close the key and record the reading, i, of the ammeter.
(iv) Place the jockey at a point T on the potentiometer wire UV such that d = UT = 30.0 cm.
(v) Close the circuit, read and record the current, I, on the ammeter,
(vi) Evaluate I\(^{1}\).
(vi) Repeat the experiment for four other values of d = 40.0 cm, 50.0 cm, 60.0 cm and 70.0 cm. In each case, record I and evaluate I\(^{1}\).
(vii) Tabulate the results
(ix) Plot a graph with d on the vertical axis and I on the horizontal axis stalling both axes from the origin (0,0).
(x) Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
(xi) From the graph determine the value I\(_{1}\), of I when d = 0. (ci) Given that=s, calculate 8.
(xii) State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(xii) Given that \(\frac{E}{\delta}\) = s, calculate \(\delta\).
(b)(i) Write down the equation that connects the resistance, R, of a wire and the factors on which it depends. State the meaning of each of the symbols.
(ii) An electric fan draws a current of0.75 A in a 240 V circuit. Calculate the cost of using, the fan for 10 hours if the utility rate is $ 0.50 per kWh.