(i) What is dielectric?
(ii) A parallel plate capacitor consists of two plates each of area 9.6 x 10\(^{-2}\)m\(^2\), separated by a dielectric of thickness 2.25 x 10\(^{-3}\) and dielectric constant 900. Calculate the capacitance of the capacitor. [ \(\varepsilon_o\) = permittivity of free space = 8.85 x 10\(^{-12}\)Fm\(^{-1}\)]
(b) (i) Which of the following devices has a higher resistance; an ammeter or a voltmeter? Give a reason for your answer.
(ii)
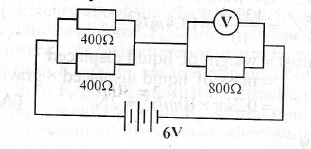
The resistance of the voltmeter in the circuit diagram illustrated above is 800\(\Omega\), Calculate the voltmeter reading.
(c)
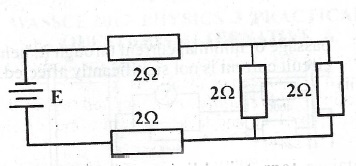
A battery of negligible internal resistance is connected to a set of resistors as illustrated in the circuit diagram above. Determine the equivalent resistance of the circuit.
(a) (i) What is nuclear fission?
(ii) State the function of each of the following ma-terials in a nuclear fision reactor:
(\(\alpha\)) graphite, (\(\beta\)) boron rods; (\(\gamma\)) liquid sodium
(b) The table below gives some of the energy levels of a hydrogen atom.
| n | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | \(\infty\) |
| E\(_n\)/\_eV\) | -13.60 | -3.39 | -1.51 | -0.85 | -0.54 | 0.00 |
(i) Draw the energy level diagram for the atom.
(ii) Determine the wavelength of the photon emitted when the atom goes from the energy state n = 3 to the ground state. [h = 6.6 x 10\(^{-34}\) Js, c = 3 x 10\(^{8}\)ms\(^{-1}\), e = 1.6 x 10\(^{-19}\)]
(c) A piece of ancient bone from an excavation site showed \(^{14}_{6}\)C activity of 9.5 disintegrations per minute per 1.0x10\(^{-3}\)kg. If a bone specimen from a living creature shows \(^{14}_{6}\)C activity of 12.0 disintegrations per minute per 1.0 x 1 0\(^{-3}\), determine the age of the ancient bone. [Half - life of \(^{14}_{6}\)C = 5572 years].
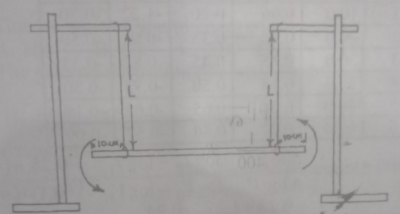
You are provided with two retort stands, two-metre rules, pieces of thread, and other necessary apparatus. ( see illustration above)
i. Set up the apparatus as illustrated above ensuring the strings are permanently 10cm from either end of the rule.
ii. Measure and record the length L = 80 cm of the two strings.
iii. Hold both ends of the rule and displace the rule slightly, then release so that it oscillates about a vertical axis through its centre.
iv. Determine and record the time t for 10 complete oscillations.
v. Determine the period T of oscillations.
vi. Evaluate log T and L.
vii. Repeat the procedure for four other values of L= 70 cm, 60 cm, 50 cm, and 40 cm
viii. Tabulate your readings.
ix. Plot a graph with log T on the vertical axis and log L on the horizontal axis.
x. Determine the slope, s, and the intercept, c on the vertical axis.
xi. State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. Define simple harmonic motion.
ii. Determine the value of L corresponding to t= 12 s from the graph in 1.

You are provided with a beaker, a thermometer, a stirrer Stopwatch/clock, measuring cylinder, table salt, water, and other necessary materials.
i. You Measure 200cm\(^{3}\) of water into the beaker.
ii. Heat the water until it boils steadily for about 2 minutes.
iii. Read and record the boiling point b\(_{0}\).
iv. Add table salt of mass M = 10.0 g to the boiling water and stir continuously until another boiling point b\(_{1}\) is attained.
v. Read and record b\(_{i}\).
vi. Evaluate \(\theta_{i}\) = (b\(_{i}\) - b\(_{0}\))
vii. Using the same mixture, repeat the procedure four more times by adding 10.0 g of salt each time to give the cumulative mass M\(_{i}\) of salt as 20 g, 30g, 40g, and 50g.
viii. In each case allow the mixture to boil steadily for at least 2 minutes then read and record the boiling point b.
ix. Tabulate your readings.
x. Plot a graph with M\(_{i}\) on the vertical axis and \(\theta_{1}\) on the horizontal axis.
xi. Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
xii. State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b) i. Define the boiling point of a liquid.
ii. What effects do impurities have on the boiling point of a liquid?

You are provided with cells, a potentiometer, an ammeter, a voltmeter, a bulb, a key, a jockey, and other necessary materials.
i. Measure and record the e.m.f E of the battery.
ii. Set up a circuit as shown in the diagram above.
iii. Close the key K and use the jockey to make a firm.
iii. Contact at J on the potentiometer wire such that PJ = x= 10cm.
iv. Take and record the voltmeter reading V and the () Corresponding ammeter reading.
v. Evalute log V and log I.
vi. Repeat the procedure for five other values of x = 20 cm, 30 cm, 40 cm, 50 cm, and 60 cm.
vii. Tabulate your readings.
viii. Plot a graph with log I on the vertical axis and log V on the horizontal axis.
ix. Determine the slope s, of the graph.
x. Determine the intercept, c, on the vertical axis.
xi. State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
(b)i. How is the brightness of the bulb affected as x increases?
ii. List two electrical devices whose actions do not obey Ohm's law.