(a) Explain the terms:
(i) thermal equilibrium;
(ii) fundamental interval.
(b) List two uses of the hydraulic press.
(c) Name the material used to reset the steel index in the Six's maximum and minimum thermometer.
(d)(i) A nursing mother prepared her baby's milk mixture at 85°C, in a feeding bottle. In order to cool it to 40°C, she immersed the bottle in an aluminium bowl of heat capacity 90 JK\(^{-1}\) containing 500 g of water at 26°C. If the mass of the mixture is 300g, calculate the specific heat capacity of the mixture. [Neglect heat losses and heat capacity of the bottle; specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J kg\(^{-1}\) K\(^{-1}\)]
(ii) (\(\alpha\)) Name two ways through which the bottle losses heat.
(\(\beta\)) Name two industrial processes in which heat exchanger is used.
(a) Define critical angle.
(b) How are anti-nodes created in a stationary wave?
(c) The angle of minimum deviation of an equilateral triangular glass prism is 46.2°. Calculate the refractive index of the glass.
(d) An illuminated object is placed in front of a concave mirror and the position of a screen is adjusted in front of the mirror but no image is obtained on the screen. Give two possible reasons for this observation.
(e) An illuminated object is placed at a distance of 75 cm from a converging lens of focal length 30 cm.
(i) Determine the image distance.
(ii) If the lens is replaced by another converging lens, the object has to be moved 25 cm further away to have its sharp image on the screen. Determine the focal length of the second lens.
(a) Explain briefly dielectric strength.
(b) An electromagnetic wave has its wavelength shorter than those of radiowave and microwave but longer than that of visible light.
(i) Identify the wave.
(ii) Name one suitable detector for the wave.
(iii) Name one source of the wave.
(c) An oil drop carrying a charge of 1.0 x 10\(^{-19 }\)C is found to remain at rest in a uniform electric field of intensity 1200 NC\(^{-1}\). Calculate the weight of the oil drop.
(d) An RLC series circuit consists of a 100\(\Omega\) resistor, 0.05 H inductor and a 25 \(\mu\) capacitor. A 220 V, 50 Hz mains voltage is applied across the circuit. Calculate the:
(i) impedance;
(ii) current. (\(\pi\) = 3.14)
(a) Explain the following terms:
(i) mass defect;
(ii) binding energy of a nucleus.
(b)(i) Assuming the wave nature of an electron, what is the effect of decreasing the speed of a photoelectron on its; (\(\alpha\)) wavelength? (\(\beta\)) energy?
(ii) A particle of friasS 4.4 x 10\(^{-23}\) kg moves with a velocity of 10\(^5\)ms\(^{-1}\). Calculate its wavelength. (h = 6.6 x 10\(^{-34}\) Js)
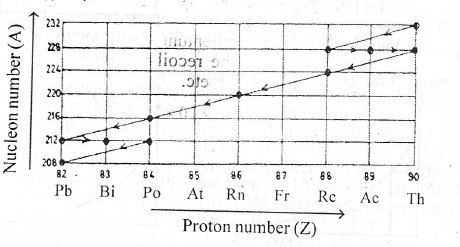
The diagram above shows part of a radioactive decay series. Use it to answer the following questions.
(i) Name a pair of isotopes.
(ii) Name the isotopes with which the series starts.
(iii) Write down a nuclear equation for two ekgmples of each of: (\(\alpha\)) alpha decay; (\(\beta\)) beta decay.
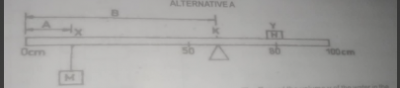
You are provided with a uniform metre rule, a knife-edge, some masses and other necessary materials.
i. Determine and record the centre of gravity of the metre rule.
ii. Fix the 100g mass marked N at a point Y, the 80cm mark of the rule using a sellotape.
iii. Suspend another 50g mass marked M at X, a distance A = 1Ocm from the 0cm mark of the rule.
iv. Balance the arrangement horizontally on the knife edge as illustrated in the diagram above.
v. Measure and record the distance B of a knife-edge from the 0cm mark of the rule.
vi. Repeat the procedure for four other values of A =15cm, 20cm, 25cm and 30cm.
vii. Tabulate your readings.
viii. Plot a graph with B on the vertical axis and A on the horizontal axis.
ix. Determine the slope, s, of the graph.
x. Also determine the intercept, c, on the vertical axis.
xi. Evaluate:
\(\propto\)) = k\(_{1}\) = (\(\frac{1 - 2s}{s}\))100
(\(\beta\)) = k\(_{2}\) = \(\frac{2c}{s}\) = 160
xii. State two precautions taken to obtain accurate results.
(b)i. Define the moment of a force about a point.
ii. State two conditions under which a rigid body at rest remains in equilibrium when acted upon by non-parallel coplanar forces.