An electron enters perpendicularly into a uniform magnetic field which has a flux density of 0.12 T This results in a magnetic force of 9.6 x 10\(^{-2}\) N on the electron. Calculate the speed of the electron as it enters the magnetic field. (e =1.6 x \(10^{19}\) C)
(a) What is doping?
(b) Explain how doping improves the conductivity of a semiconductor
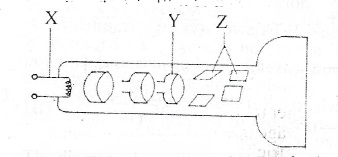
The diagram above illustrates a cathode ray tube. Identify the components X, Y, and Z.
(a) Explain the term net force.
(b) Define the principle of conservation of linear momentum and state one example of it.
(c) A ball of mass 200 g released from a height of 2.0 m hits a horizontal floor and rebounds to a height of 1.8 in. Calculate the impulse received by the floor. (g = 10 ms\(^{-2}\)).
(d) A body of mass 20 g performs a simple harmonic motion at a frequency of 5 Hz. At a distance of 10 cm from the mean position, its velocity is 200 cms\(^{-1}\). Calculate its:
(i) maximum displacement from the mean position;
(ii) maximum velocity;
(iii) maximum potential energy. (g = 10 ms\(^{-2}\) \(\pi\) = 3.14)