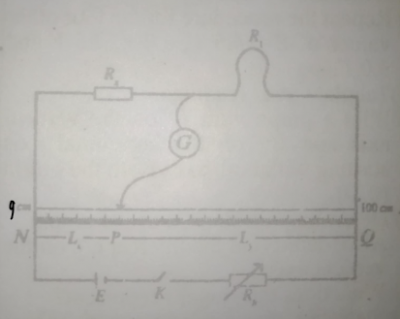
(a) You are provided with two resistance wires labelled: A and B, standard resistor, R\(_x\) = 1 \(\Omega\), metre bridge, cell of emf,E, Rheostat R\(_h\), galvanometer and apparatus as shown.
Use the circuit diagram above as a guide to perform the experiment.
(i) Connect R\(_x\) in the left-hand gap of the metre bridge, a length L = 100 cm of the wire in the right-hand gap and the other apparatus shown.
(ii) Determine and record the balance point P on the metre bridge wire NQ
(iii) Measure and record L\(_x\) = NP and L\(_y\) = PQ
(iv) Evaluate R\(_1\) = \(\frac{L_y}{L_x}R_x\)
(v) Repeat the procedure for four other values of L = 90cm, 80cm, 70cm, and 60cm. In each case, determine and record the balance point, P and evaluate R\(_1\)
(vi) Repeat the experiment with the second wire B. Obtain the balance point P and evaluate R\(_2\) in each case
(vii) Tabulate the readings
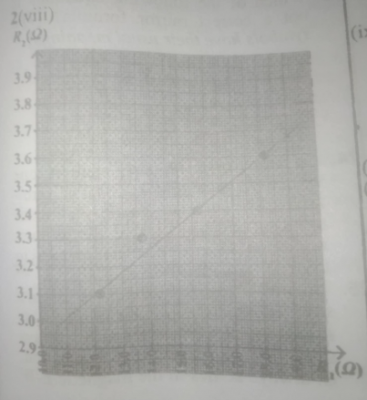
(viii) Plot a graph of R\(_2\) on the vertical axis and R\(_1\) on the horizontal axis
(ix) Determine the slope, s, of the graph
(x) Evaluate K = \(\sqrt{s}\)
(xi) State two precautions taken to ensure accurate results.
b(i) State two advantages of potentiometer over voltmeter for measuring potential difference
(ii) Define internal resistance of a cell.
(vii)
| L(cm) | L\(_x\)(cm) | L\(_y\)(cm) |
R\(_1\) = (\(\frac{L_y}{L_x})R_x\)\(\Omega\) |
L\(_{x2}\) | L\(_{y2}\) |
R\(_2\) = \(\frac{L_{y2}}{L_{x2}}R_x\)\(\Omega\) |
| 100.0 | 5.2 | 94.8 | 18.2 | 21.5 | 78.5 | 3.6 |
| 90.0 | 6.0 | 94.0 | 15.7 | 22.5 | 77.5 | 3.4 |
| 80.0 | 6.8 | 93.2 | 13.7 | 23.4 | 76.6 | 3.3 |
| 70.0 | 7.6 | 92.4 | 12.2 | 24.5 | 75.5 | 3.1 |
| 60.0 | 8.4 | 91.6 | 10.9 | 25.6 | 74.4 | 2.9 |
(viii) SEE THE GRAPH ABOVE
(ix) Slope = \(\frac{Δ R_2}{Δ R_1}\) = \(\frac{3.5 - 3.3}{17.0 - 14.6}\) = \(\frac{0.2}{2.4}\) = 0.083
(x) K = \(\sqrt{0.083}\) = 0.2881
(xi) I Tight connection/clean terminal was ensured II. Key removed when readings were not being taken.
b(i) I. A potentiometer can be used for measuring the internal resistance of a cell and also to compare the e.m.f. of two cells. II. A potentiometer gives the exact value of potential difference across any two points in a circuit.
(ii) It refers to the opposition to the flow of current offered by the cells and batteries themselves resulting in the generation of heat.
Contributions ({{ comment_count }})
Please wait...
Modal title
Report
Block User
{{ feedback_modal_data.title }}