(a) Explain the term uniform acceleration
(b)(i) Sketch and describe the velocity-time graph for the motion of a ball from the time it is projected vertically upwards until it returns to the point of projection.
(ii) Neglecting air resistance and using ycur sketch, explain how the acceleration of free fall due to gravity g, and the maximum height attained when the ball is projected vertically upwards can be determined.
(c) A stone is projected vertically upwards with a velocity of 20ms\(^{-1}\). Two seconds later, a second stone is similarly projected with the same velocity. When the two stones meet, the second one is rising at a velocity of 10ms\(^{-1}\). Neglecting air resistance, calculate the:
(i) length of time the second stone is in motion before they meet,
(ii) velocity of the first stone when they meet (Take g as 10ms\(^{-2}\))
(a) A body is said to be moving with uniform acceleration when its time rate of increase of velocity is constant. It is measured in m/s\(^2\). It is a vector quantity.
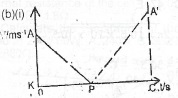
The above sketch shows the v-t graph of the ball. The velocity decreases uniformly from A to zero (p) at the top of K its flight in a time kp. P , Va It then increases in velocity uniformly as it returns to the point of projection A.
(ii) The magnitude of the slope of the line AP = g or Ap\(^-\) = g, where g = acceleration of free fall due to gravity. The height attained when the ball is thrown up is equal to the area of the triangle AKP. The distance it falls from its maximum height is equal to the area of the triangle A\(^-\)PC which is equal to triangle AKP.
(c)(i) The second stone moves upwards and its acceleration g = 10m/s\(^2\). From equation v = u - gt
10 = 20 - 10t -10 = -10t
t = 1
The second stone has been in air for 1s before they met.
(ii) The first stone has been moving for (1 + 2)s = 3s
From equation v = u + gt
= 2 - (10 x 3) = 20 - 30 = -10m/s
The minus sign means the first stone is moving down and its velocity is 10m/s.
Contributions ({{ comment_count }})
Please wait...
Modal title
Report
Block User
{{ feedback_modal_data.title }}