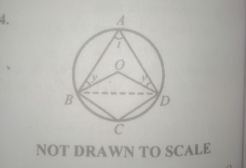
In the diagram, ABCD is a circle O. The quadratic OBCD is a rhombus such that \(\angle\)ADO = \(\angle\)OBA = y and \(\angle\)BAD = t. Find;
(a) the value of t;
(b) the value of y;
(c) \(\angle\)ADC.
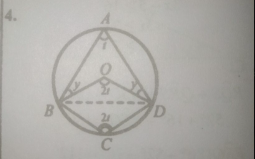
(a) to find t
\(\angle\)BCD = \(\angle\)BOD = 2t (angle at the centre = twice that at the circumference)
\(\angle\)BCD = \(\angle\)BAD = 180º (opposite angles of a cyclic quad. are supplementary)
2t + t = 180º
3t = 180º
t = 60º
(b) to find the value of y
\(\angle\)BOD = 2t = 2 x 60 = 120º
\(\angle\)BOD = \(\angle\)ODB (equal radii)
⇒ \(\angle\)OBD +\(\angle\)ODB + 2t = 180º ( sum of <s in a \(\triangle\))
2\(\angle\)OBD + 2(60) = 180º
\(\angle\)OBD = \(\angle\)ODB = 30º
Consider \(\triangle\)BAD
60 + (y + 30 ) + (y + 30) = 180 ( sum of <s in a triangle)
60 + 30 + 30 + 2y = 180º
2y = 180 - 120 = 60º
y = \(\frac{60}{2}\) = 30º
(c) to find \(\angle\)ADC
\(\angle\)OBD + \(\angle\)ODB + \(\angle\)BOD = 180º
2\(\angle\)ODB = 180 - \(\angle\)BOD
2\(\angle\)ODB = 180 - 2t
2\(\angle\)ODB = 180 - 120
2\(\angle\)ODB = 60º
\(\angle\)ODB = \(\frac{60}{2}\) = 30º
\(\angle\)ADC = \(\angle\)ADO + \(\angle\)ODB + \(\angle\)BDC
\(\angle\)ADC = 30º + 30º + 30º = 90º
Contributions ({{ comment_count }})
Please wait...
Modal title
Report
Block User
{{ feedback_modal_data.title }}